| [1] Weimer R, Ettrich M, Renner F, et al. ATG induction in renal transplant recipients: Long-term hazard of severe infection is associated with long-term functional T cell impairment but not the ATG-induced CD4 cell decline. Hum Immunol.2014;75(6): 561-569.
[2] Donckier V, Craciun L, Miqueu P, et al. Expansion of memory-type CD8+ T cells correlates with the failure of early immunosuppression withdrawal after cadaver liver transplantation using high-dose ATG induction and rapamycin. Transplantation.2013;96(3):306-315.
[3] Esposito L, Kamar N, Tkaczuk J, et al. Long-term evolution of lymphocytes subsets after induction therapy based on continuous versus discontinuous administration of anti-thymocyte globulins in renal-transplant patients. Transplant Proc.2005;37(2):785-787.
[4] Ponticelli C. Basiliximab: efficacy and safety evaluation in kidney transplantation. Expert Opin Drug Saf.2014;13(3): 373-381.
[5] Holowiecki J. Indications for hemalopoietic stem cell transplantation.Pol Arch Med Wewn.2008;118(11):658-663.
[6] Barbari A, Stephan A, Masri MA. Donor specific transfusion in kidney transplantation:effect of different immunosuppressive protocols on graft outcome.Transplant Proc.2001;33(5): 2782-2785.
[7] Crop MJ, Baan CC, Korevaar SS, et al. Donor derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress alloreactivity of kidney transplant patients.Transplantation.2009;87(6):896-906.
[8] Figliuzzi M, Cornolti R, Perico N, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve islet graft function in diabetic rats.Transplant Proc.2009;41(5):1797-1800.
[9] Sheng Sun D, Iwagaki H, Ozaki M, et al. Prolonged survival of donor-specific rat intestinal allograft by adiministration of bone-marrow-derived immature dendritic cells.Transplant Immunol.2005;14(1):17-20.
[10] 平季根,严春寅,吕金星.CTLA4-Ig腺病毒基因局部转染诱导大鼠肾移植免疫耐受[J].实验动物与比较医学,2007,27(1):45-47.
[11] He W, Fang Z ,Wang F, et al. Galectin-9 significantly prolongs the survival of fully mismatched cardiac allografts in mice. Transplantation.2009;88(6):782-785.
[12] Cicora F, Mos F, Paz M, et al. Clinical experience with thymoglobulin and antithymocyte globulin-Fresenius as induction therapy in renal transplant patients: a retrospective study. Exp Clin Transplant.2013;11(5):418-422.
[13] van den Hoogen MW, Kho MM, Abrahams AC, et al. Effect of a single intraoperative high-dose ATG-Fresenius on delayed graft function in donation after cardiac-death donor renal allograft recipients: a randomized study.Exp Clin Transplant. 2013;11(2):134-141.
[14] Brokhof MM, Sollinger HW, Hager DR, et al. Antithymocyte globulin is associated with a lower incidence of de novo donor-specific antibodies in moderately sensitized renal transplant recipients.Transplantation.2014;97(6):612-617.
[15] 蔡俊超,Paul I.Terasaki.免疫诱导治疗可改善器官移植后长期预后:美国器官分配联合网络注册数据分析[J].中华移植杂志:电子版,2010,4(4):275.
[16] Bumgardner GL, Hardie I, Johnson RW, et al. Results of 3-year phase III clinical trails with daclizumab prophylaxis for prevention of acute rejection after rennal transplantation. Transplantation.2001;72(5):839-845.
[17] 黎磊石.在肾移植中应用抗CD25单抗诱导治疗的体会[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2005,14(1):47-48.
[18] 陈忠华,徐逸.CD25单克隆抗体在临床肾移植中的应用[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2005,14(1):48-49.
[19] 郑凯,谭建明,吴卫真,等.舒莱在肾移植免疫诱导治疗中有效性和安全性研究[J].免疫学杂志,2007,23(5):556-558.
[20] 顾梅,张昆鹏,关炳星,等.巴昔利单抗与抗胸腺细胞球蛋白在肾移植早期效果的比较[J].中国医院药学杂志,2009,29(8):659-662.
[21] Goggins WC, Pascual MA, Powelson JA, et al. A prospective, randomize, clinical trail of intraoperative versus postoperative Thymoglobulin in adult cadaveric renal transplant recipients. Transplantation.2003;76(5):798-802.
[22] Brennan DC, Flavin K, Lowell JA, et al. A randomized, double-blinded comparison of thymoglobulin versus atgam for induction immunosuppressive therapy in adult renal transplant recipients.Transplantation.1999;67(7):1011.
[23] 郑军华,闵志廉,朱有华,等.抗胸腺淋巴细胞球蛋白对尸肾移植排斥反应的预防及治疗作用[J].第二军医大学学报,1999,20(10): 814-815. |
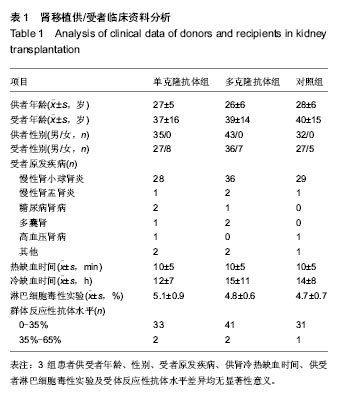
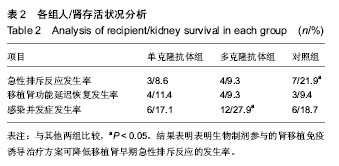
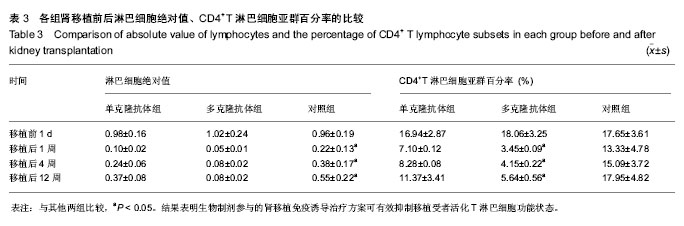
.jpg)